Paradontosis treatment
Periodontology translated from the Greek language is the study of what is "around the tooth”, periodontal diseases, their diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Tooth surrounding tissues are: gums, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone.
Periodontitis (formerly known as parodontosis) is a progressive gingival and periodontal tissue inflammation disease. This is the most common cause of tooth loss in subjects above 35 years of age. It was found that around 80% older than 30 years people have varying degrees of periodontitis (parodontosis). In most cases, this disease does not cause pain, progresses slowly, thus many people do not even know that they have it.
The main cause of periodontitis is hard and soft dental plaque and bacteria which reside in it. Soft plaque eventually hardens to form tartar. Tartar cannot be cleaned with a toothbrush – it has to be removed by dental hygienist or periodontist. Initially, tartar and bacteria within destroy gum tissues and gum inflammation begins. Gums become red and swollen, starts to bleed. Over the time gums recede along with the bone, resulting in periodontal pockets’ formation and denudation of roots. Plaque and tartar fill the pockets. The process involves increasingly deeper tissues. In advanced stages of periodontal disease, teeth mobility increases and teeth are eventually lost.
Dental X-ray:
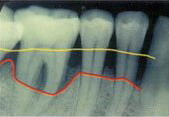
Yellow – healthy bone margin, Red – bone recession
Untreated periodontitis (parodontosis) poses a negative effect on the entire body (e.g. heart – vascular system). It was found that disease can provoke premature birth. Thus, treatment of periodontitis is mandatory. Damaged gums should be treated as soon as possible.
Main preventive measure of periodontitis is quality dental cleaning and regular professional oral hygiene (once every 6 months). Good oral hygiene is your cheapest dentist! :)
Smoking (especially!), human body's hormonal changes (puberty, pregnancy, menopause), diabetes, cardiovascular disease, certain medications, chemotherapy increase the risk of periodontal disease.
Periodontal disease treatment depends on the severity of the disease. It may be:
- non-surgical (conservative),
- surgical.
A team of qualified specialists treat periodontitis at our dental clinic “Pilėnė“ in Vilnius. Recently, thanks to laser technology, less traumatic treatment is available, allowing patients to avoid surgical treatment of the periodontal disease.





